Need help? Write to us info@hqlifting.com
- Charging Accessories
- Lifting accessories
- Steel Cable
- Beam cart
- Turnstile for load securing
- Load Ratchet Strap
- Lifting current
- Chain for Load Lifting
- Lifting equipment
- Slings
- Steel Cable Tensioner
- Polyester slingshot
- Load binders
- STEEL HOOK
- Steel Cable Clamp
- Electric winch
- Permanent magnets
- Steel Cable Clamp
- moitão
- Carabiners
- Screw With Eyelet
- Lifting Clamp
- Talha Manual
- Uncategorized
Call our consultants or chat online
+86 151 4514 5178
Complete Eye Bolt Buying Guide: Tips and Insights
What are eye bolts?
Eye bolts are essential components in various applications, especially in material handling, where it is necessary to pull loads away from or toward the center of the eye. Despite their simple design, they are made of forged, tempered, and quenched steel. Typically, an eye bolt consists of a threaded shaft and a ring or eye at one end. They can be screwed into structures such as wood, steel, or concrete and are usually secured with a nut. Eye bolts are designed to create a connection point where ropes, cables, or shackles can be securely attached for lifting operations.

The eye bolts come in various sizes, materials, and finishes.
Standard Eyelet Screws
A standard eye bolt is a shoulderless type that comes with a nut. It is designed to pass through a hole, being secured at the back with the provided nut. Common eye bolts are intended only for straight vertical tension or to support suspended loads. They should not be subjected to side or angular loads, as they may bend or break. For angular lifts, the use of shoulder eye bolts is recommended.
Shoulder Eye Screws
Eye bolts with shoulder, also known as flange eye bolts, feature a shoulder or support collar that provides greater stability at the base of the eye. This design allows them to be used with slings at an angle, supporting angular loads. However, it is important to note that capacity decreases with different loading angles. Proper installation is crucial. If the shoulder is not firmly seated against the mounting surface, the bolt should only be used for vertical lifting, just like a regular eye bolt. Variations include long shank shoulder eye bolts and machine eye bolts, which have a fully threaded shank, eliminating the need for a nut and being threaded directly into tapped holes.
Eye Screws Wood Thread
Eye bolts for wood, also known as wood thread eye bolts, are designed to be screwed into wood. Due to the wide variability in the density and condition of the wood, these eye bolts generally do not have defined working load limits.
Forged Eyelet Screws
The forged eye bolts feature a forged eye, offering high hardness and strength for heavy lifting applications. They are made of high-strength carbon steel, subjected to forging and annealing processes, which increase their thermal conductivity, ductility, and durability. These bolts are ideal for use in cold climates, maintaining their structural integrity under these conditions. They typically receive surface finishes such as anodizing, hot-dip galvanizing, and galvanization for enhanced corrosion resistance.
Stainless Steel Eye Bolts
Stainless steel eye bolts contain a high chromium content, forming a passive layer on the surface to prevent corrosion. Compared to galvanized carbon steel eye bolts, stainless steel eye bolts have a superior surface finish, making them more suitable for applications such as decks, architecture, and marine use.
How to measure an eye bolt?
Understanding eye bolts starts with knowing their dimensions. Measurements are usually taken below the inner diameter of the eye and take into account the length of the shank. Common specifications include:
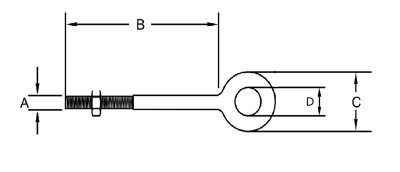
- Rod diameter (thread): (A)
- Rod length: (B)
- Outer diameter of the eyelet: (C)
- Inner diameter of the eyelet: (D)
For more detailed information about related components, you may find our Rigging Shackle Guide useful.
Installation Guide and Eye Bolt Specifications
Main Dimensions of Eye Bolts
When selecting eye bolts, the eye diameter (D) and the overall length (E) are important, but the diameter (A) and length (B) of the shank are even more crucial. These factors affect the working load limit and determine compatibility with the thickness of the material where the eye bolt is installed. For detailed information on dimensions, refer to the eye bolt size chart in the hqlifting catalog.
Calculating the Load Capacity of Eye Bolts
Eye bolts come with different working load limits to handle varying weights. It is essential not to exceed the load capacity of the eye bolt, which corresponds to its safe lifting load in the vertical direction of the shank. The nominal load capacity of the eye bolt decreases as the angle of the lifting cable relative to the vertical increases:
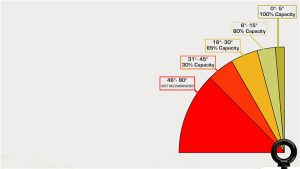
- 5 degrees:Maintains 100% of load capacity
- 15 degrees:Reduces to 80% of load capacity
- 30 degrees:Reduces to 65% of load capacity
- 45 degrees:Reduces to 30% of the load capacity
- 46+ degrees:Not recommended
Proper Installation of Eye Bolts
Proper installation is as important as choosing the right eye bolt. Here are some installation tips:
- Evaluate the material thickness to ensure that the length of the eye bolt is sufficient to pass through completely.
- Tighten the nut until the eye bolt is firmly secured and the base of the eye is in firm contact with the mounting surface.
- Use steel washers to fill gaps in the unthreaded part of the rod, ensuring that the total thickness of the washers does not exceed one thread pitch.
Hqlifting hopes this guide is useful in the selection and installation of eye bolts. For more information, visit the hqlifting website.
Share:

June Han /founder and designer
The co-founder of Hqlifting, sales director, amateur writer about fitness business






